1. Those interested in learning about the latest trends in the use of LLM (Large Language Models) and Generative AI in the data industry.
2. Individuals interested in Self-service Analytics/BI tools that enable practitioners to analyze data without the assistance of data experts.
3. Those curious about how prominent Self-Service Analytics players like Tableau, Power BI, and HEARTCOUNT are incorporating LLM into their products.
Introduction: Data Democratization and Self-service Analytics
The need for Self-service Analytics/BI is growing steadily to enhance the data literacy and utilization levels within enterprises.
It's a BI concept where end-users utilize data directly without the assistance of IT departments to create charts, derive insights, and monitor changes.
It aims to prevent the phenomenon where vast amounts of data produced and stored by companies are only consumed by a few data experts and instead promotes data democratization, enabling all members to create value from data.
In 2023, along with the commercialization of large language models (LLMs), there were significant changes for players in the Self-service Analytics market. Let's explore what happened and what changes are expected in 2024!
Self-service Analytics Market Overview
Growing Self-service Analytics Market
As the data market continues to grow, the Self-service Analytics and Self-service BI markets are growing alongside it. According to Fortune Business Insights, the size of the Self-service Analytics/BI market was approximately $48.8 billion in 2022, and it's predicted to reach a market size of $200 billion by 2030. Additionally, Gartner predicts that by 2024, 75% of enterprises will adopt Self-service Analytics/BI.
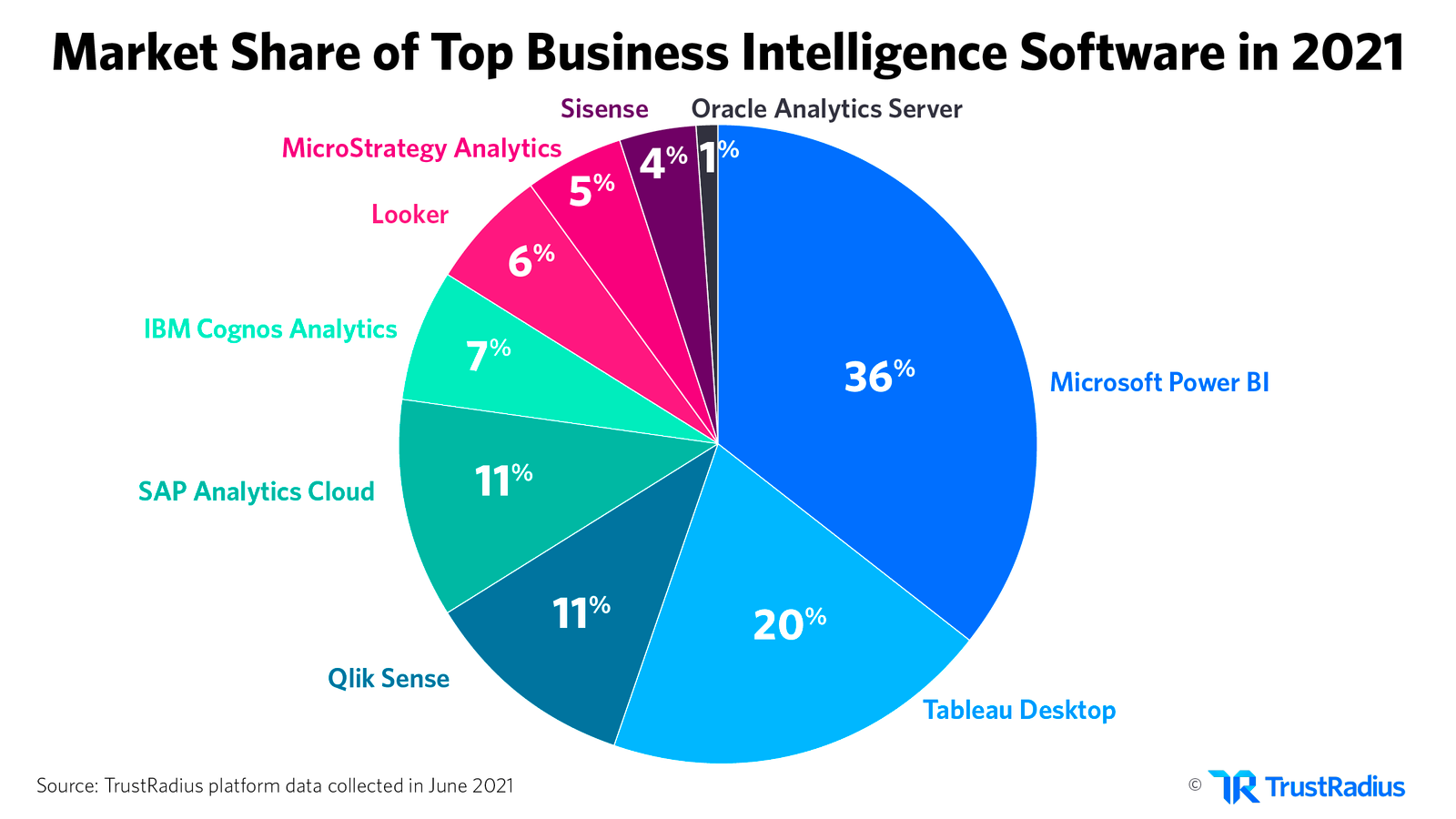
Key Players in Self-service Analytics
The major players in the Self-service Analytics market are Power BI and Tableau. According to TrustRadius data from 2021, Power BI and Tableau hold over half of the market share combined, with 36% and 20%, respectively.
Moreover, Gartner classified key products in the market based on their criteria in the "Magic Quadrant for Analytics and Business Intelligence Platforms" published on May 23rd last year. Forrester also categorized products in their "The Forrester Wave™: Augmented Business Intelligence Platforms, Q2 2023" published on June 13th last year.
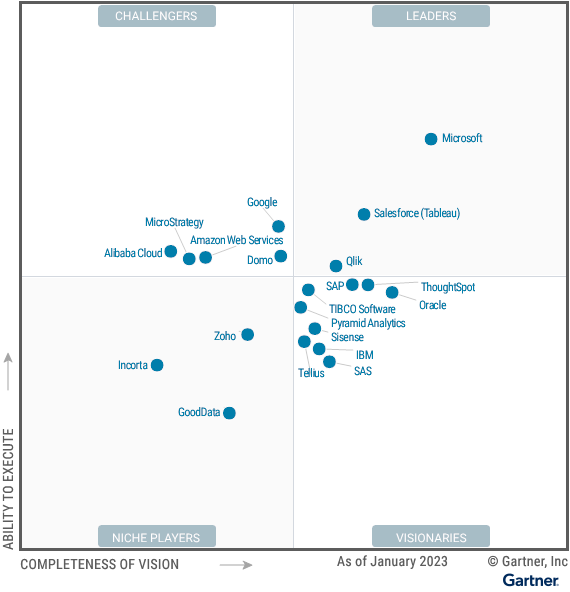
Gartner classified products in the market into quadrants. Microsoft (Power BI), Salesforce (Tableau), and Qlik (Qlik View, Qlik Sense) are positioned as Leaders. Additionally, Thoughtspot and Sisense in the Augmented Analytics market, and Oracle, IBM, SAP, and SAS are categorized as Visionaries. Google Looker, MSTR, and AWS are positioned as Challengers.
Key Trends in the Market
Emergence of LLMs and BI + Augmented Analytics
In 2023, the hottest topic in the data industry/market was undoubtedly Large Language Models (LLMs). The commercialization of OpenAI's ChatGPT and GPT 3.5 marked the beginning, followed by many tech giants introducing their models. Moreover, with the popularity of Open Source LLMs through platforms like Hugging Face, companies are accelerating their efforts to adopt LLMs for their businesses.
Self-service Analytics market is no exception. Key players are seamlessly integrating LLMs into their products. The most significant change in the market due to this phenomenon is the blurring boundary between Self-service Analytics and Augmented Analytics products. The existing products that touted Self-service Analytics mostly had the characteristics of BI. With the emergence of LLMs, users can now easily access and utilize existing features based on natural language. Let's look at some examples from key players.
Tableau: Tableau GPT & Tableau Signal
Tableau combined Einstein GPT, previously developed for Salesforce's other product Einstein Discovery, with Tableau. Although not commercially available yet, the key features include: 1. Converting natural language input requirements into SQL in Tableau Prep, a data manipulation/preparation solution. 2. Automatically detecting and interpreting key changes in metrics (Pulse) and providing visualizations and interpretations for analysis questions inputted in natural language (Pulse Q&A). Tableau Pulse is generally available since February 22nd.
PowerBI: Copilot
Microsoft has already integrated Copilot (based on GPT-4) into several of its products. Power BI is one of them. PowerBI Copilot offers similar features to Tableau. For example, it can instantly create suitable charts for user-inputted dashboard requests in natural language, interpret questions asked in natural language within dashboards, and convert user inquiries into Power BI's unique data analysis language, DAX (Data Analysis Expression).
Other Products
Thoughtspot: Thoughtspot was a dominant player in the augmented analytics market based on NLP (Natural Language Processing) even before the emergence of LLMs. With the arrival of LLMs, Thoughtspot also launched Sage, integrated with GPT-3. Sage provides appropriate visualizations and natural language summaries for user's natural language questions.
MicroStrategy: MicroStrategy also unveiled Microstategy AI, incorporating LLM, last October. It offers features like LLM-based automatic answer provision, automatic dashboard creation, and automatic SQL generation.

Qlik Sense: Another strong player in the Self-service Analytics realm, Qlik Sense, released Insight Advisor integrated with LLM. It provides visualizations and explanations for user-inputted natural language questions and allows sharing results with other members of the organization via MS Chat.
Taking a Breath Amidst the Fierce LLM Battle
As seen, the influence of large language models is disrupting the entire Self-service Analytics market. With every player in the market adopting LLMs and competing, it seems that Generative AI is increasingly becoming the 'standard.' Nevertheless, amidst this fierce competition, it's essential to take a moment to look beyond the flashy and powerful facade of LLMs.
#1. LLM Can't Replace Everything
Shall we take a brief detour? About two weeks ago, a company called Rabbit unveiled a demo video of their new product, Rabbit 1. Within just 10 days of its release, the video garnered over 4.6 million views, capturing the market's attention. This product ambitiously aims to maximize generative AI technology to replace traditional smartphones.

The market's response has been mixed. While the product showcases impressive performance (image recognition, voice recognition, LLM) and a futuristic UX, many remain skeptical about whether it can truly replace traditional smartphones.
In reality, relying solely on natural language interfaces to utilize functions may not always be convenient. There are cases where a well-defined and planned user experience, integrated with simple button operations, is sufficient. However, there will undoubtedly be areas where the strengths of language models are maximized (such as understanding user language context and semantics).
Ultimately, opinions suggest that the user experience presented by Rabbit R1 will likely integrate with smartphones in the market.
What about Self-service Analytics? While LLM is indeed an innovation disrupting the IT/data market as a whole, it can't replace all existing data analysis methodologies and processes.
Aspects such as the background of data generation processes, meticulously defined business logic/KPIs, and interpreting charts and analysis results in the context of business still require a human touch.
In the end, it seems likely that LLM will be utilized in enhancing the usability of Self-service Analytics products to assist users in accessing and utilizing existing functionalities more effectively.
#2. Addressing Hallucination
One of the major issues highlighted in the commercialization of LLM is hallucination.
Errors occurring during the processing of information by AI
LLMs confidently delivering inaccurate responses, despite their lack of accuracy and reliability, can leave a negative impression in terms of accuracy and reliability. Especially in fields like data analysis that demand precise and reliable numbers, this phenomenon becomes even more critical.
Do you remember the incident from the summer of '23? Microsoft unveiled a data analysis platform named 'Fabric' with a dazzling demo, chanting slogans like "Discover hidden insights with AI," and "Feel the power of AI with just a flick of your finger."
However, the incident where LLM generated inaccurate SQL statements in response to user questions during the demo video, the part that garnered the most attention, can't be simply dismissed as a mishap.
It's predicted that with the release of GPT-5 by OpenAI later this year, the phenomenon of hallucination will decrease. However, from the perspective of Self-service Analytics companies, minimizing dependence on giant tech companies like OpenAI is preferable.
#3. Private LLM, Fine-Tuning, and RAG
To address the issue of hallucination and reduce dependence on giant tech companies (such as Public LLM from OpenAI), the value of Private LLM is expected to increase in the Self-service Analytics market.
Models modified and enhanced by companies according to their own purposes based on LLMs publicly released as open source
Fine-tuning techniques, where companies modify models using internal data (expensive), and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), where instead of modifying the model, references to other text data are used during answer generation, are key aspects of Private LLM.
Through these efforts, 1) companies can offset hallucination issues, 2) reduce dependence on giant tech companies, and 3) cut costs. Unless they are giant tech companies like Microsoft, they can't afford the astronomical costs (in the billions) of creating models themselves. Moreover, domestic large corporations/financial institutions are very sensitive to security issues, often banning the use of tools like ChatGPT internally.
Ultimately, Private LLM is expected to dominate the Self-service Analytics/Self-service BI market.
Closing: How HEARTCOUNT Utilizes LLM
We've explored the LLM-infused Self-service Analytics market together! It seems that the progress of generative AI will continue across the industry this year as well. We look forward to seeing what developments and changes will occur in the Self-service Analytics market.
HEARTCOUNT meticulously examines the potential and limitations of LLM and is conducting various research and development efforts related to LLM to ensure that users can use HEARTCOUNT more conveniently and accurately.
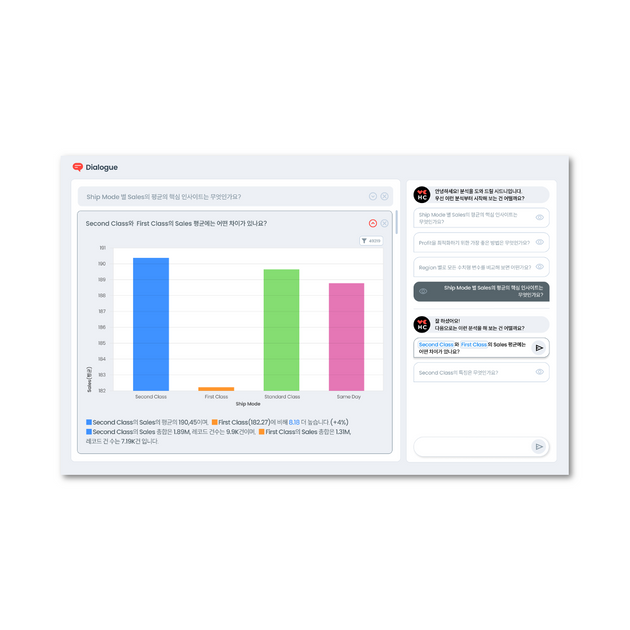
Last year, as part of a series of features for automating questions and answers related to data, we introduced Text-to-SQL (TTS) and Dialogue features that convert natural language into SQL and provide interactive analysis, respectively (you might want to check out the article we shared earlier this year!).
We invite you to join us in realizing the vision of data analysis for all users this year and look forward to your continued support :)
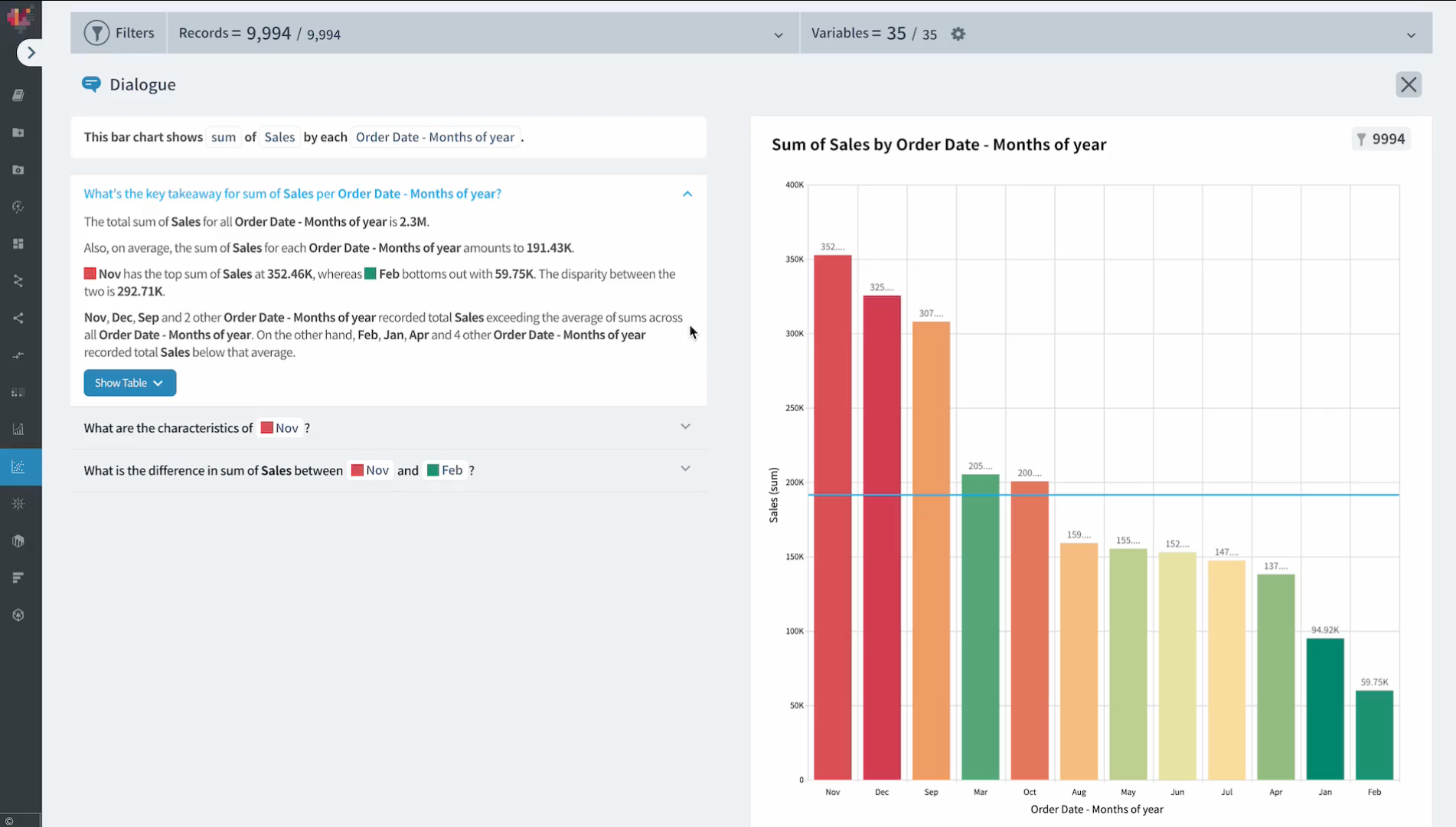
Log in now with your Google account to try it out.